Modo Overview
Here's the improved version of your documentation text:
Modo is a simple and convenient state-based navigation library for Jetpack Compose. It offers a flexible and powerful way to manage navigation in your application.
The UI of Modo navigation is defined by
NavigationState, which is a structure ofScreenandContainerScreen. You can easily modifyNavigationStateto suit your needs from any part of your application.
Main Idea
Navigation is a Graph
Each integration of Modo is a rooted tree (wiki) that can be displayed as follows:
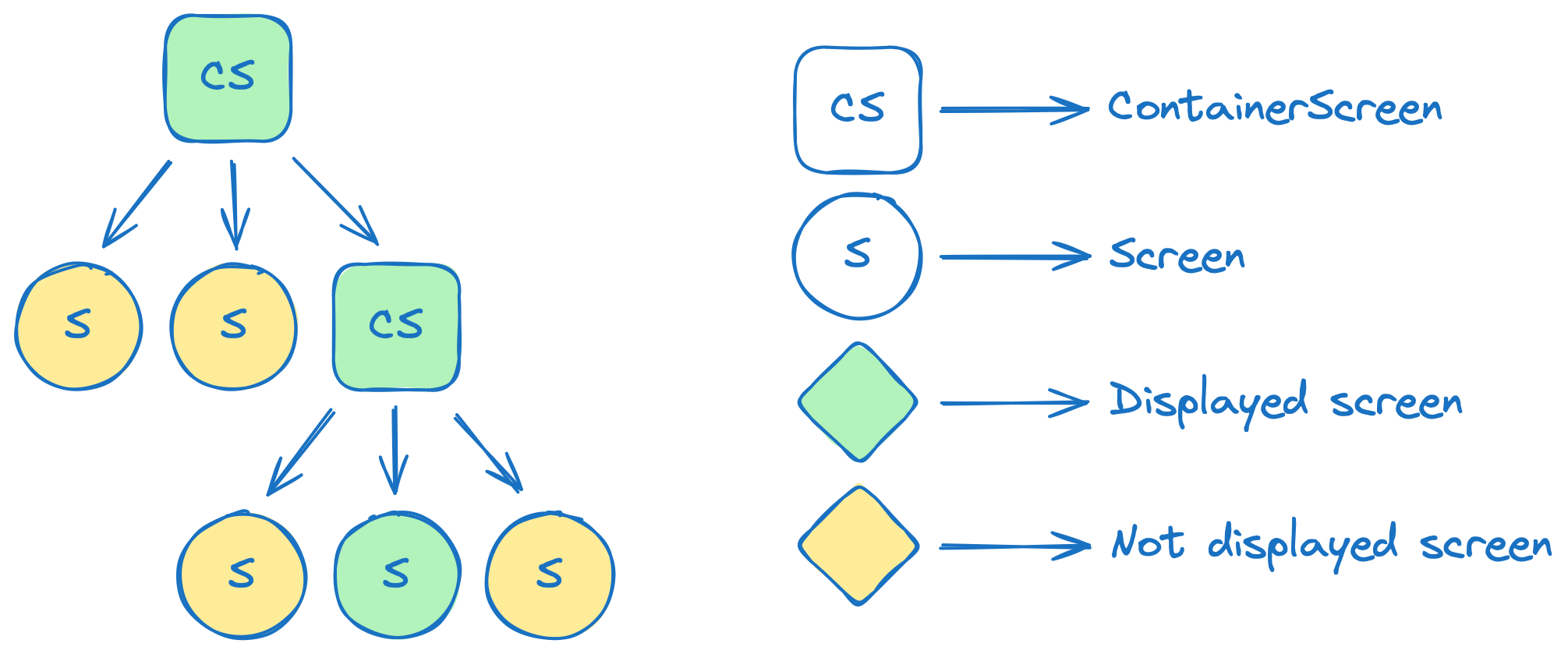
Each node is a
ScreenorContainerScreen.Leaf nodes are
Screens.Inner nodes are
ContainerScreens. They can contain otherScreens orContainerScreens in theirnavigationState.The root node is a
RootScreen. You can have multiple roots in your app. See How to integrate Modo for details.
Convenient Navigation
Modo is an easy-to-use library. Here are some of the most-used features of Modo navigation:
Screenis the basic unit of the UI. It displays content defined in the overriddenfun Content(modifier: Modifier).@Parcelize class SampleScreen( override val screenKey: ScreenKey = generateScreenKey() ) : Screen { @Composable override fun Content(modifier: Modifier) { Text( text = "Hello, Modo! Screen №$screenIndex", modifier = modifier ) } }To navigate between screens in a stack, simply call
forward()andback()onStackScreen, which is an implementation ofContainerScreen.// 1. Taking the nearest stack screen val stackNavigation = LocalStackNavigation.current // 2. Performing navigation val onForwardClick = { stackNavigation.forward(SampleScreen()) }You can easily change
NavigationStateas needed by callingdispatch(action: (StackState) -> StackState)onNavigationContainer:navigation.dispatch { oldState -> StackState( oldState.stack.filterIndexed { index, screen -> index % 2 == 0 && screen != oldState.stack.last() } ) }To integrate Modo with your application, use
rememberRootScreeninside aFragmentorActivity. You can useDefaultStackScreenas a default stack implementation.setContent { val rootScreen = rememberRootScreen { DefaultStackScreen(SampleScreen()) } rootScreen.Content(Modifier.fillMaxSize()) }
Getting Started
To get started with Modo, check out our Quick Start Guide and explore the sample application to see how Modo can simplify your navigation needs.